Solving multi-agent safe optimal control with distributed epigraph form MARL
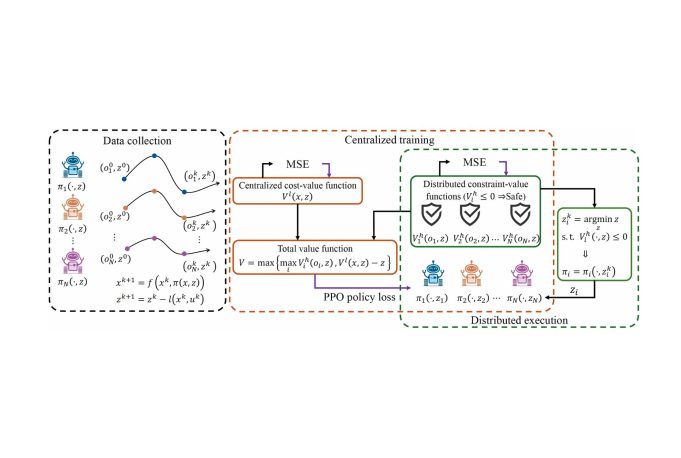
REALM researchers propose a novel multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) framework in the centralized training distributed execution paradigm using the epigraph form, improving training stability.
Authors: Songyuan Zhang, Oswin So, Mitchell Black, Zachary Serlin, and Chuchu Fan
Citation: Robotics: Science and Systems 2025
Abstract:
Tasks for multi-robot systems often require the robots to collaborate and complete a team goal while maintaining safety. This problem is usually formalized as a constrained Markov decision process (CMDP), which targets minimizing a global cost and bringing the mean of constraint violation below a user-defined threshold. Inspired by real-world robotic applications, we define safety as zero constraint violation. While many safe multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) algorithms have been proposed to solve CMDPs, these algorithms suffer from unstable training in this setting.
To tackle this, we use the epigraph form for constrained optimization to improve training stability and prove that the centralized epigraph form problem can be solved in a distributed fashion by each agent. This results in a novel centralized training distributed execution MARL algorithm named Def-MARL. Simulation experiments on 8 different tasks across 2 different simulators show that Def-MARL achieves the best overall performance, satisfies safety constraints, and maintains stable training. Real-world hardware experiments on Crazyflie quadcopters demonstrate the ability of Def-MARL to safely coordinate agents to complete complex collaborative tasks compared to other methods.