Imaging of dynamic plasma-combustion interactions through a transparent electrode
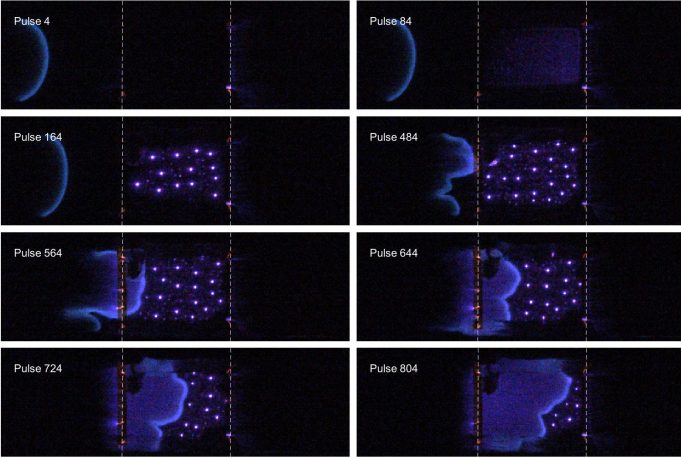
Graduate student Colin Pavan and Prof. Carmen Guerra-Garcia (Aerospace Plasma Group) use novel transparent electrode technology to image the interactions between a combustion flame and plasma. Their approach reveals that the plasma discharge alters both the flame’s speed and curvature, while the flame impacts the discharge’s uniformity and the motion of microdischarges.
Authors: Colin A. Pavan and Carmen Guerra-Garcia
Citation: (2025) Frontiers in Physics, 13, 1654714
Abstract:
A common platform for studying plasma-assisted ignition and combustion uses a quartz reactor with the plasma applied in a dielectric barrier discharge configuration. The line-of-sight typically used in such a setup, for optical diagnostics and imaging, is transverse to the dominant electric fields. This visualization angle makes the quantification of the dynamic bidirectional interactions between plasma and combustion processes incomplete. Drawing inspiration from the literature on pattern formation in dielectric barrier discharges operated with inert gases, the authors introduce a novel approach: employing transparent indium tin oxide (ITO) electrodes to directly visualize the interaction between a propagating laminar flame and a pulsed nanosecond dielectric barrier discharge. The approach reveals features of the interaction that were previously inaccessible: the discharge alters both the flame’s speed and curvature, while the flame, in turn, impacts the discharge’s uniformity and the motion of microdischarges. This brief research report demonstrates how the use of transparent electrodes in plasma-assisted combustion enhances our ability to explore this complex two-way interaction.