Specifications
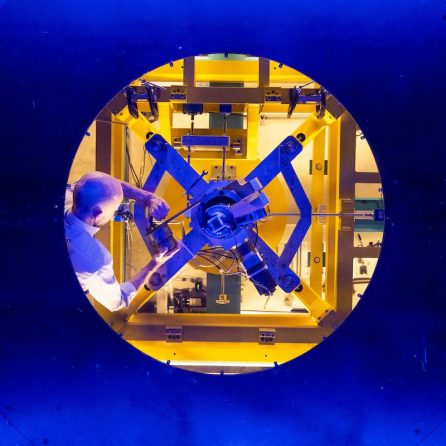

Since its dedication in 1938, the Wright Brothers Wind Tunnel has become a campus landmark used for education, research, industry, and outreach. In 2017, MIT AeroAstro announced it would replace the tunnel with a brand-new facility. Today, MIT is home to the most advanced academic wind tunnel in the country, capable of reaching wind speeds up to 230 miles per hour (mph), with the largest test section in U.S. academia.
Quick Links
- Wind Tunnel User Agreement
- Model−Mount Strut
- Model Mounting Platform
- Model Mount Options on Main Balance
At a Glance
| Characteristics | |
|---|---|
| Airspeed range | 15 mph – 230 mph |
| Dynamic pressure range | 0.5 psf – 135 psf |
| Flow conditioning | 8:1 contraction ratio 4 anti-turbulence screens Honeycomb + screen in fourth-corner vanes Flow-circuit heat exchanger |
| Drive | 2500 hp motor, VFD control to 600 rpm max 16 ft diameter fan, 17 blades, BLI design Leaned + swept stator, 7 cambered vanes |
| Test section | Dimensions: 12 x 7.75 x 18 ft Corner fillets, tapering 14…10 in At nearly ambient pressure All-glass side walls, 5 windows in ceiling |
| Model mounting (on external balance) | Metric post and pitch pushrod inside non-metric aero fairing, allowing +/- 30 deg pitch and +/-30 deg yaw OR Metric flange just under floor, allowing +/- 30 deg yaw |
| Model mounting (on floor turntable) | Non-metric floor turntable, allowing +/- 45 deg yaw |
| Equipment | Built-in y, z traverse, reaching entire test section Portable 2-axis traverse, 3 x 4 ft reach Pitot-static probes 3-hole and 5-hole probes Pitot rakes Electronic pressure scanning sensors, up to 1 psid 1-axis and 2-axis inclinometers |
| MATLAB-based test control software | Can control and drive nearly all tunnel functions via GUI and/or custom high-level MATLAB scripts Can interrogate tunnel airflow instruments, main balance, and any custom user instrument output Automates wind-off tares Allows real-time data viewing Logs all data with time stamps Allows data export in a wide variety of formats |
| External Balance Load Limits (Moment reference point is at center of test section) | |
|---|---|
| Lift | +1500 lb / -500 lb |
| Drag | +/- 225 lb |
| Sideforce | +/- 750 lb |
| Pitching moment | +/-500 ft-lb |
| Yawing moment | +/-500 ft-lb |
| Rolling moment (strut mount) | +/-500 ft-lb |
| Rolling moment (flange mount) | +/- 1500 ft-lb |
What is unique about the Wright Brothers Wind Tunnel?

Screened expanding turning vanes

Boundary layer ingesting fan

State-of-the-art test section

Faster data collection
Descriptive Data
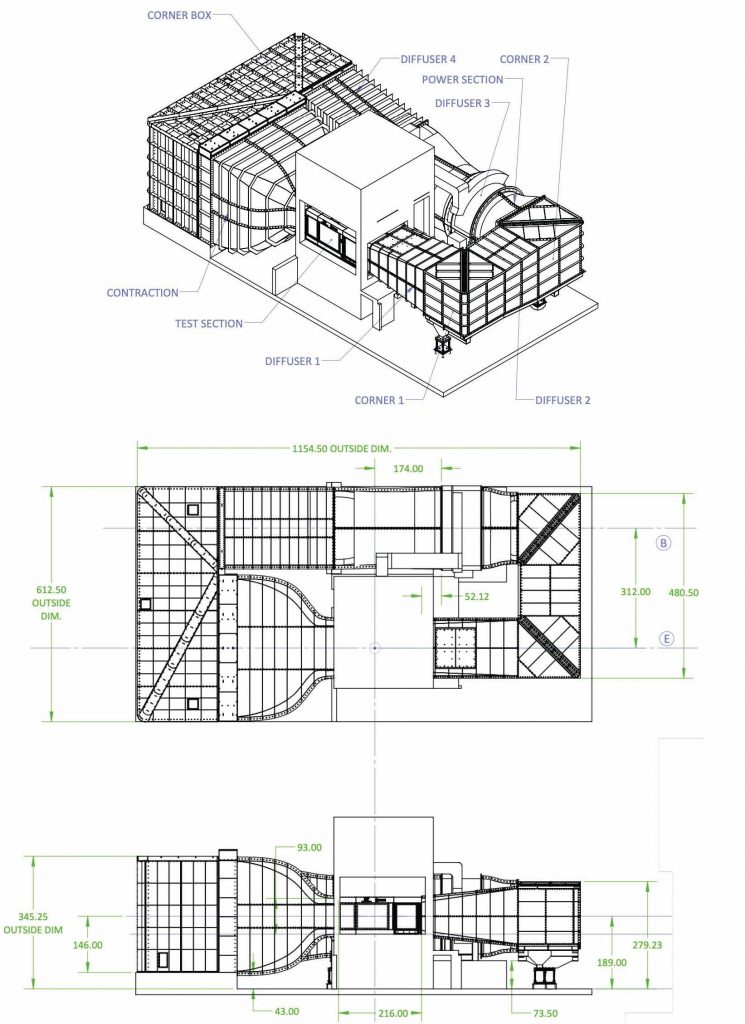
Wind Tunnel

| Configuration | Closed Circuit |
| Contraction | 8:1 |
| Flow Conditioning | Honeycomb, screen in Corner 4, 4x screens in settling chamber |
| Corner 1 | Airfoil vanes, conventional |
| Corner 2 | Airfoil vanes, expanding (1:1.17) |
| Corner 3 | Formed vanes, conventional |
| Corner 4 | Formed vanes, screened, expanding (1:1.875) |
| Cooling System | 40% propylene glycol, 217 tons |
| Cooling Coils | 3 |
Test Section

| Type | Closed wall, neutral pressure |
| Inside Width | 12 feet 0 inches |
| Inside Height | 7 feet 9 inches |
| Length | 18 feet |
| Cross Sectional Area | 90 sqft |
| Doors | 2 |
| Wall Taper | 0 degrees |
| Boundary Layer Compensation | Tapered corner fillets |
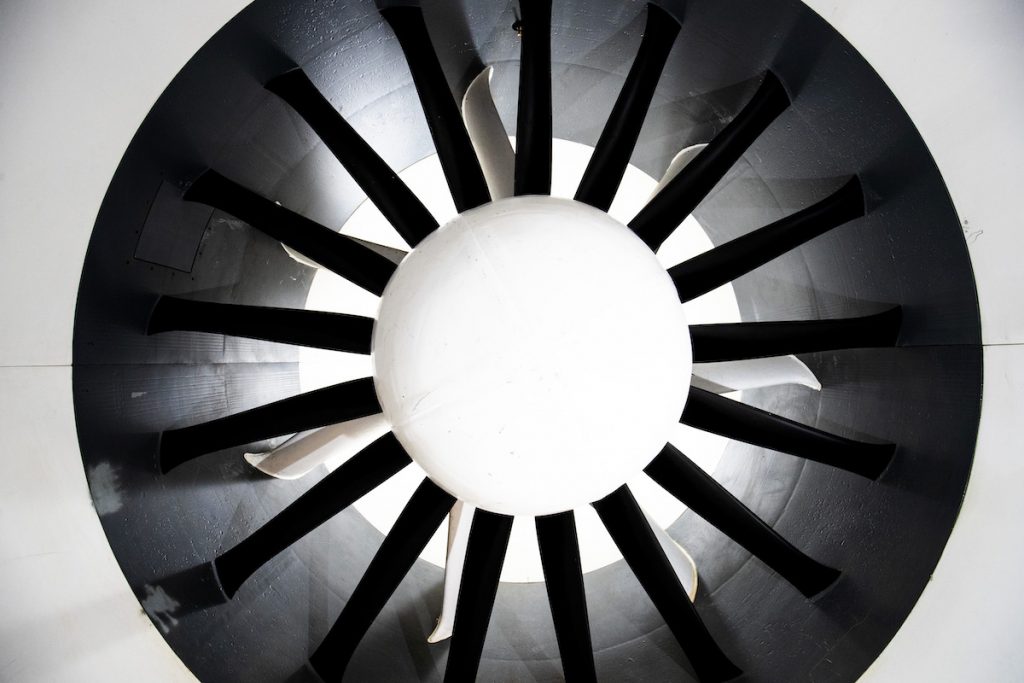
Fan System

| Type | Fixed pitch, rigid in plane |
| Number of Fans | 1 |
| Number of Rotor Blades | 17 |
| Rotor Diameter | 16 feet |
| Tip Speed @ 100% RPM | 502 FPS |
| Number of Stator Vanes | 7 |
| Drive Configuration | Direct drive |
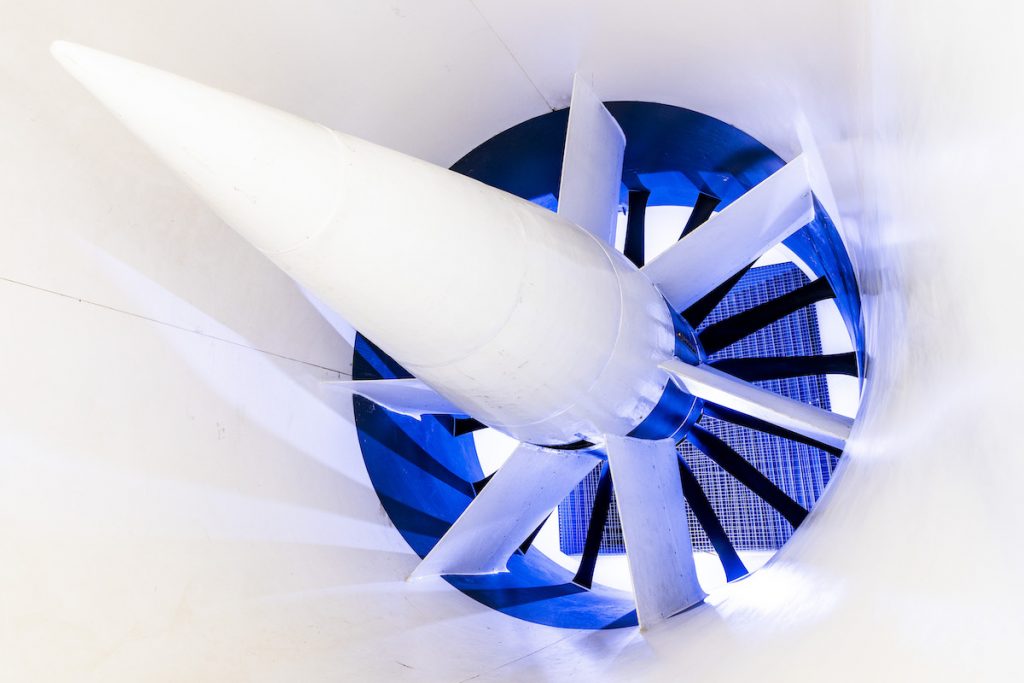
Motor

| Number of Motors | 1 |
| Make | ABB |
| Type | AMI 560L8P BAFH |
| Power | 2,500 HP |
| Volts | 4,000 |
| Amps | 345 |
| Phase | 3 |
| Hertz | 40.3 |
| RPM @ 100% | 600 |
Variable Frequency Drive

| Number of Drives | 1 |
| Make | Rockwell Automation |
| Type | PowerFlex 7000 |
| Power | 2,500 HP |
| Line Volts | 4,160 |
Limitations
This section includes operation limitations, instrument markings, and basic placards required for safe operation of the wind tunnel and associated systems.
Airspeed Limits
| Never Exceed Airspeed (VNE) | 230 MPH |
| Maximum Continuous Airspeed | 210 MPH |
| Maximum Airspeed with Doors Open or Removed | 40 MPH |
Motor Limits
| Maximum Motor Speed | 600 RPM |
| Maximum Motor Current | 345 FLA |
| Maximum Power (Continuous) | 2,500 HP |
| Maximum Winding Temperature | 160 Deg C |
| Maximum Bearing Temperature | 105 Deg C |
Fan Limits
| Maximum Fan Speed | 600 RPM |
| Maximum Vibration | 0.3 in/s |
Test Section Limits
| Maximum Air Temperature | 125° F |
| Minimum Air Temperature | 15° F |
| Maximum Air Pressure | 21 psf (4 in-wg) |
| Minimum Air Pressure | -21 psf (-4 in-wg) |
Continuous operation approved with test section doors fully open or removed up to 40 MPH. Operations above 40 MPH require test section doors to be installed and closed.
Note: Operations with test section doors opened or test section doors removed increase turbulence levels, put additional stresses on the wind tunnel equipment, and can lead to premature component wear.
Equipment Limits

Operation prohibited with inoperative safety instruments, equipment protection instruments, or emergency stop buttons and LEDs.
Caution: Operation with inoperative safety instruments and equipment protection instruments can lead to catastrophic failure of critical components, injury, or death.
Operation prohibited with maintenance hatches open or removed.
Tampering with or altering the PLC system is prohibited.
Tampering with or altering the VFD system is prohibited.
Crew Requirements

Minimum crew: 1 operator
The wind tunnel operator must be endorsed as qualified or under the supervision of an operator endorsed as qualified and have received training on normal procedures and emergency procedures of the wind tunnel.
The wind tunnel operator must be stationed or positioned within arm’s reach of a wind tunnel emergency stop button while the wind tunnel is in operation.
Operational Limits

Operations with an empty test section are approved.
Operations with a model in the test section are approved as long as the model is secured and the operator is able to maintain visual contact with the model while the wind tunnel is in operation.
Operations with one or more occupants in the test section are limited to 35 MPH.
